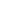
煎饼馃子 Chinese savoury crepe
近日,天津市餐饮行业协会批准了《天津市地方传统名吃 制作加工技术规范 天津煎饼馃子》。这一规范从5月26日起实施。
煎饼馃子有了技术规范 薄饼直径不小于38cm
这份标准规定了天津煎饼馃子的术语与定义、原、辅料要求、制作场所及设备要求、加工过程卫生及人员要求、制作工艺要求、标识、包装、运输与贮存等内容。
我们来看看这份标准都做了哪些规定:
煎饼馃子有了技术规范 薄饼直径不小于38cm
❶ 天津煎饼馃子的原料(ingredients)是绿豆面(green bean flour)、小米面(millet flour)、鸡蛋、面粉等;
❷ 辅料(dressings)包括面酱、葱末(chopped scallions)、辣酱(chili sauce)、腐乳(酱豆腐)、芝麻;
❸ 馃子又称油条(deep-fried dough sticks);馃箅(bì)儿是油炸面制食品,薄、脆,形状方形;
❹ 刷子摊成的薄饼直径应在38~45cm;
❺ 成品建议两小时内食用(to be consumed within 2 hours)。
煎饼馃子分会秘书长宋冠鸣在接受中国日报采访时表示:
"Our move has triggered debates over whether it is meaningful to unify the cooking standards of the food," Song said.
宋冠鸣说,“我们的这一举措引发了大量讨论,网友质疑是否有必要为煎饼制定统一的制作标准。”
The renowned Chinese snack jianbing guozi, deep-fried dough sticks rolled in a thin pancake(also known as Chinese savoury crepe), has a history of 600 years in Tianjin and has become a favorite gourmet flavor worldwide, Song said.
宋冠鸣介绍称,煎饼馃子作为中国知名小吃在天津有600年的历史,而且已经成为世界各地都喜爱的一种美食。
煎饼馃子有了技术规范 薄饼直径不小于38cm
"However, it's not our aim to make it standard like KFC fast food. We just aim to better regulate the cooking process, techniques and health safety for the time-honored Tianjin style in its hometown."
“但我们的目的并不是把煎饼做成肯德基这样的标准化快餐。我们只是希望更好地规范这一历史悠久的天津名吃的加工过程、制作工艺和食品卫生。”
宋冠鸣称,制定团体标准的初衷,是为了让天津煎饼馃子在传统化、统一化、标准化的道路上走得更远。
The association indicated that it doesn't mean to regulate the proportions of the ingredients, the taste of the sauce or make every stand selling it provide the same flavor.
煎饼馃子分会表示,他们不会限定作料的用量和面酱的味道,也不会要求每个煎饼摊做出同一个口味的煎饼。
However, it is dedicated to protecting the techniques of the most traditional jianbing guozi.
但协会将致力于保护传统煎饼制作工艺。
中华文明探源工程 the project aimed at tracing the origins of Chinese civilization
The project aimed at tracing the origins of Chinese civilization released its archaeological research results on Monday. According to its findings, Chinese civilization can be traced back more than 5,000 years based on the large-scale archaeological research in many domestic ruins.
中华文明探源工程28日发布考古研究成果,在国内多个遗址进行的大规模考古研究证实,中华文明可以追溯到5000多年以前。
中国国家文物局副局长关强介绍,探源工程是以考古调查发掘(archaeological research)为获取相关资料的主要手段,以现代科学技术为支撑,采取多学科交叉研究(multidisciplinary scientific research)的方式,揭示中华民族5000年文明起源与早期发展的重大科研项目。该工程由中国社科院考古研究所(the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences' Institute of Archaeology)、北京大学考古文博学院(Peking University's School of Archaeology and Museology)牵头,联合近70家科研院所、高等院校和地方考古研究机构共同参与。
多年来,探源工程专家聚焦良渚、陶寺、石峁、二里头等都邑性遗址(capital city-level sites),以田野考古(field archaeology)工作为中心,为实证5000年中华文明提供重要证据。
经过多年研究,专家们对中华文明起源和早期发展的过程进行了梗概式描述。
Signs of civilization emerged around 5,800 years ago in areas of the Yellow River, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the West Liao River in Northeast China
距今5800年前后,黄河、长江中下游以及西辽河等区域出现了文明起源迹象;
Around 5,300 years ago, some regions along the Yangtze River, the Yellow River and the western bank of Liaohe River (in Northeast China) stepped into the age of civilization.
距今5300年以来,长江、黄河以及辽河西岸部分地区陆续进入了文明阶段;
A more mature civilization took shape in central China around 3,800 years ago and spread cultural influence around, becoming the focus and leader in formation of the Chinese civilization.
距今3800年前后,中原地区形成了更为成熟的文明形态,并向四方辐射文化影响力,成为中华文明总进程的核心与引领者。