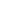
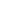
藏医药浴法 Lum medicinal bathing of Sowa Rigpa

请看例句:
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) inscribed on Wednesday China's Lum medicinal bathing of Sowa Rigpa on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
28日,联合国教科文组织将中国"藏医药浴法"列入人类非物质文化遗产代表作名录。
28日,正在毛里求斯首都路易港举行的联合国教科文组织保护非物质文化遗产政府间委员会第13届常会通过审议,批准中国申报的"藏医药浴法"列入联合国教科文组织人类非物质文化遗产代表作名录(Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity)。委员会在决议中指出,该遗产项目"凸显了有关自然界和宇宙的传统知识的重要性,提供了人类与环境间可持续关系的积极例证(underline the importance of traditional knowledge concerning nature and the universe and offer a positive example of the sustainable relationship between humans and their environment)"。随着藏医药浴法的列入,我国共有40个项目列入联合国教科文组织非物质文化遗产相关名录。
藏医药浴法,藏语称"泷沐",是中国藏族人民以土、水、火、风、空"五源"生命观和隆、赤巴、培根"三因"健康观及疾病观为指导,通过沐浴天然温泉或药物煮熬的水汁或蒸汽,调节身心平衡,实现生命健康和疾病防治的传统知识和实践(traditional knowledge and practices of bathing in natural hot springs, herbal water or steam to adjust the balance of mind and body so as to ensure one's good health or treat illnesses)。作为藏医学"索瓦日巴(Sowa Rigpa, Tibetan Medicine)"的重要组成部分,藏医药浴法以青藏高原的雅砻河谷和宗喀山脉的藏族农牧区为集中传承区域,广泛流布于西藏、青海、四川、甘肃、云南等地的藏区,为保障藏族民众的生命健康和防治疾病发挥着重要作用。
中国文化和旅游部副部长张旭表示,藏医药浴法与中国藏族民众的日常生活息息相关(have an important bearing on the everyday life of the Tibetan people in China)。这一遗产项目既体现了藏民通过沐浴防病、疗疾的民间经验(folk experience in disease prevention and treatment),也是传统藏医理论(traditional Tibetan medicine theories)在当代健康实践中的继承和发展。藏医药浴法列入联合国非遗名录有助于促进不同民族关于生命健康和尊重自然的对话(encourage dialogue on health and respect for nature between different ethnic groups),体现了人类与环境之间的可持续关系。
[相关词汇]
非物质文化遗产 intangible cultural heritage
藏族文化 Tibetan culture
生命观 life view
水疗 hydrotherapy
文化多样性 cultural diversity
传统文化教育 traditional culture education